The Animals
Blue and Gold Macaw
General Info
Common Name: Blue and Gold Macaw
Scientific Name: Ara ararauna
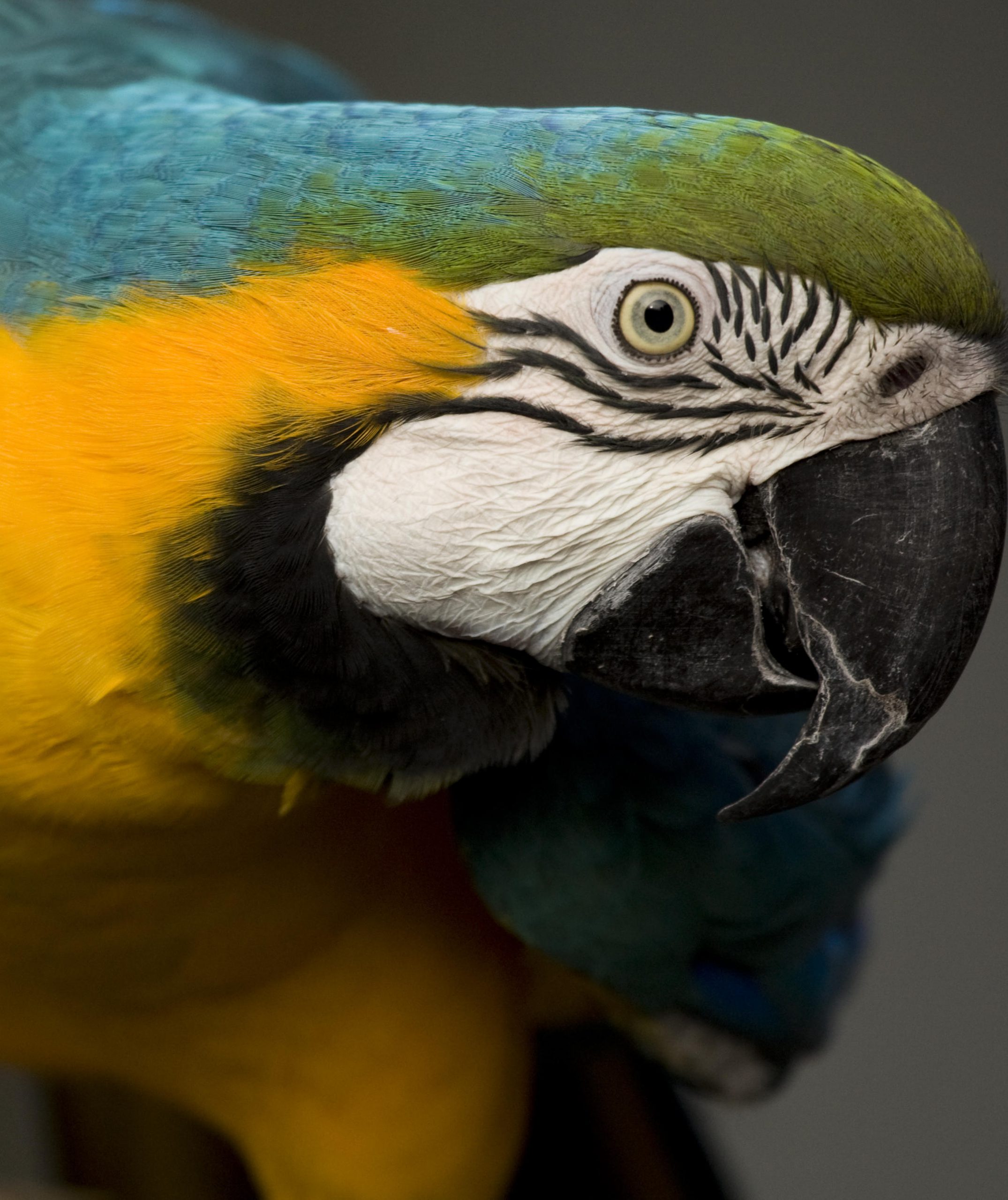
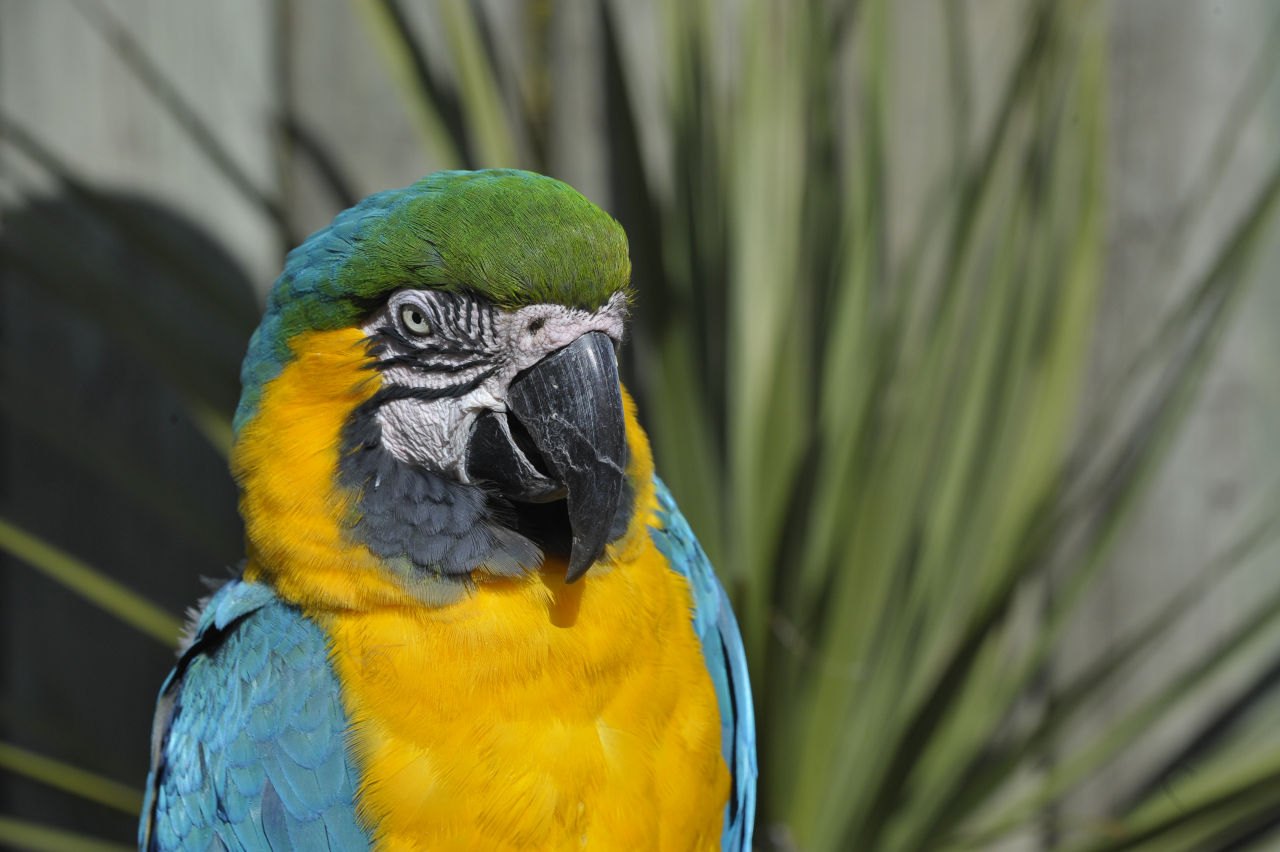
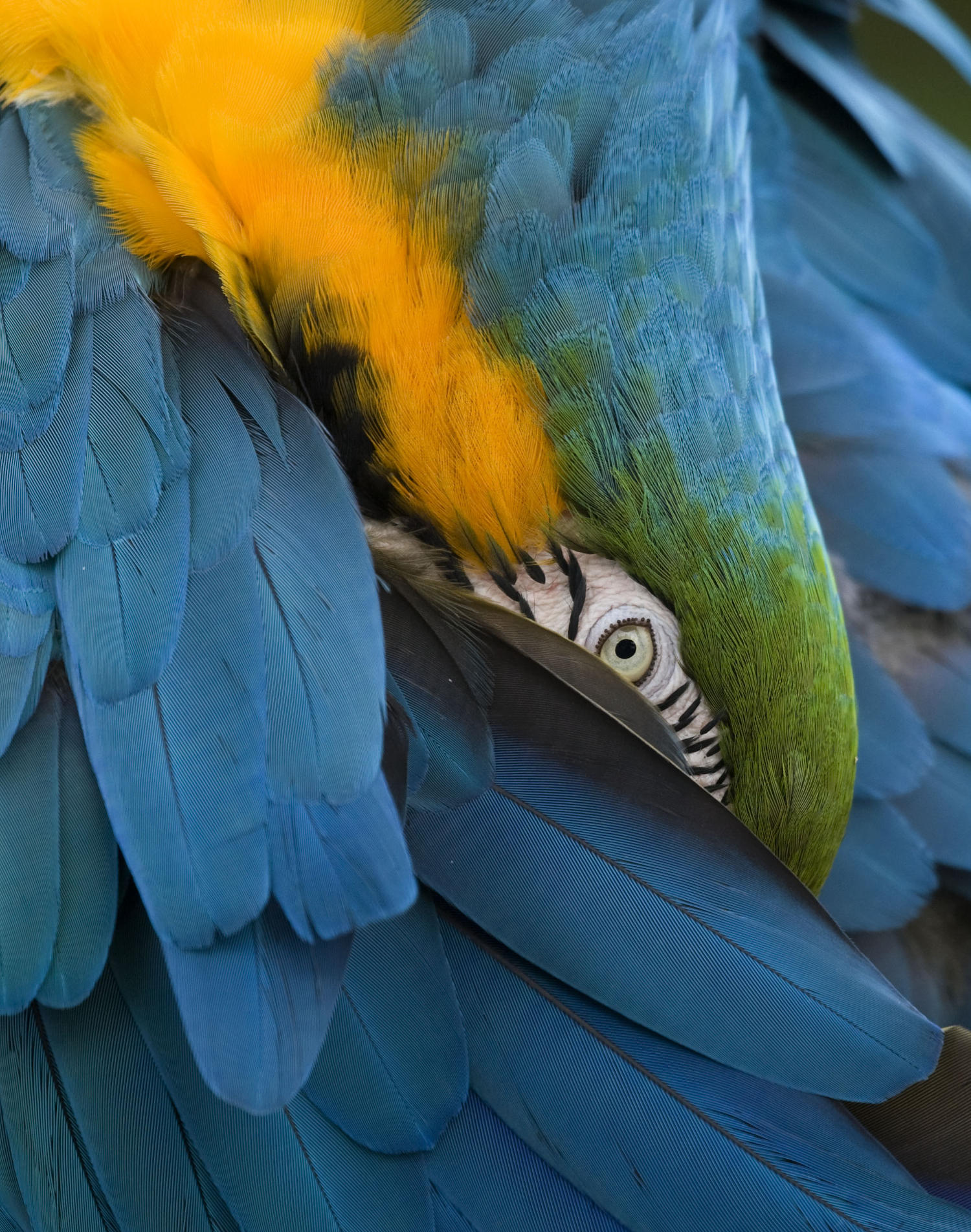
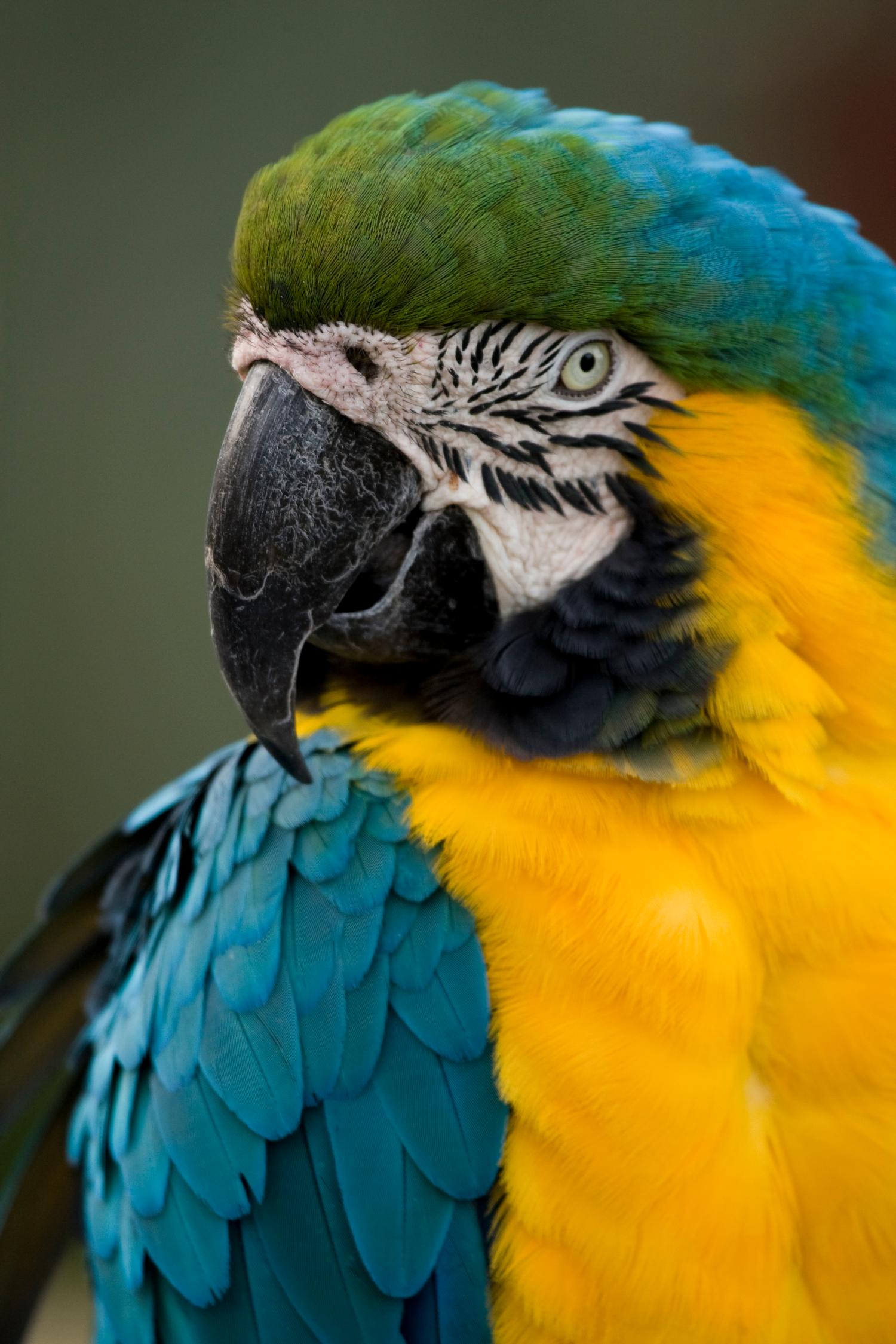
Physical Appearance: Males and females are sexually monomorphic. Plumage is bright blue above, mostly golden-yellow below. Long blue and yellow tail. Cheek-patch bare white with fine lines of dark feathers. Black throat feathers with green feathers on forehead. Large black/grey beak.
Length/Weight: : 76-89 cm. long (including tail) with a 90-113 cm. wingspan, 900-1,200 gms.
Lifespan: Can live 30-35 years in the wild. 50+ years in captivity.

Environment
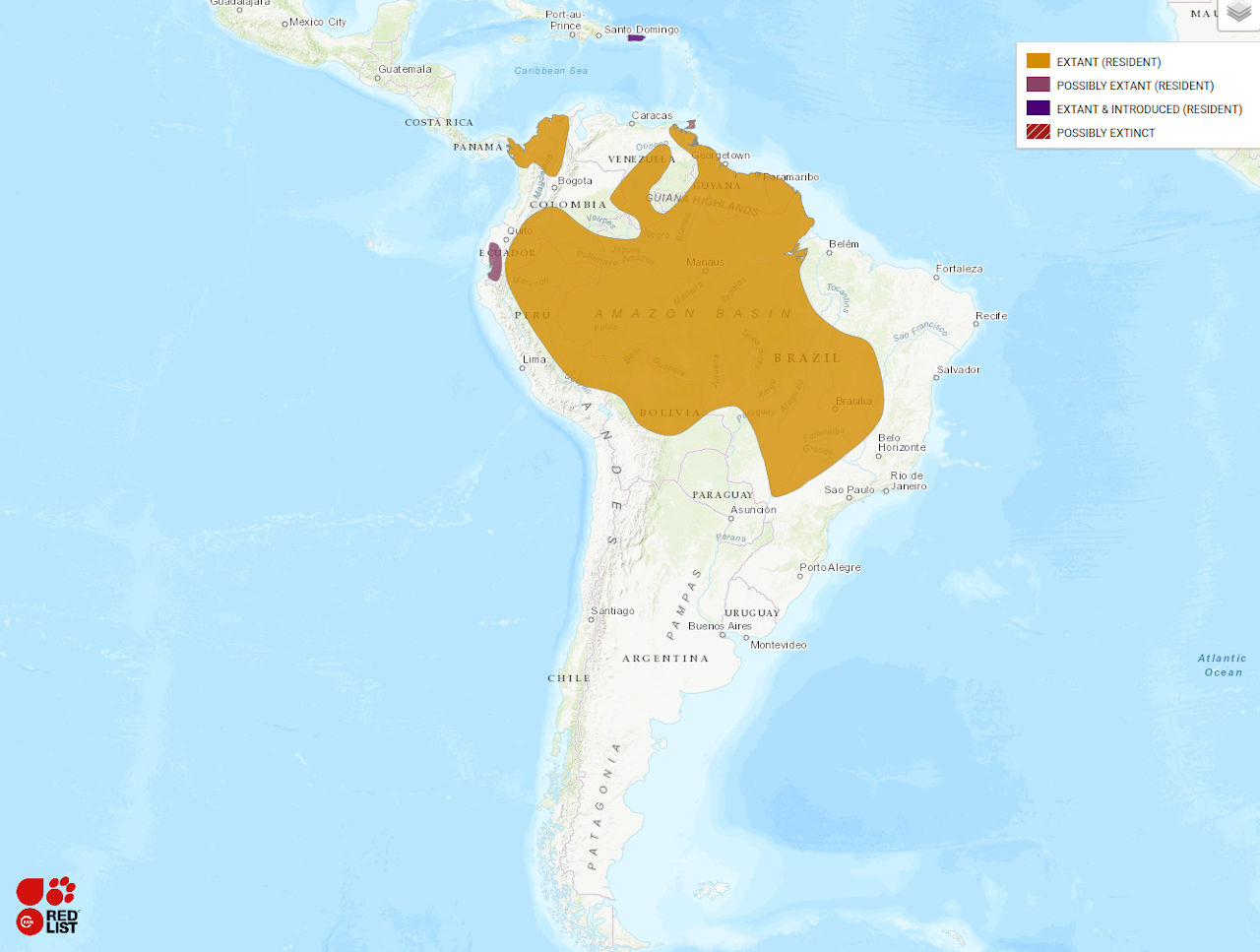
Range: Largest distribution is within central, South America (Brazil, Venezuela, Bolivia, and Paraguay) with a population in Columbia and east Panama.
Habitat: Found in wooded areas near water, edge of lowland humid forests, gallery, palm and swamp forests. Has been seen to forage in open country and live as high up as 1,640 feet.
Diet
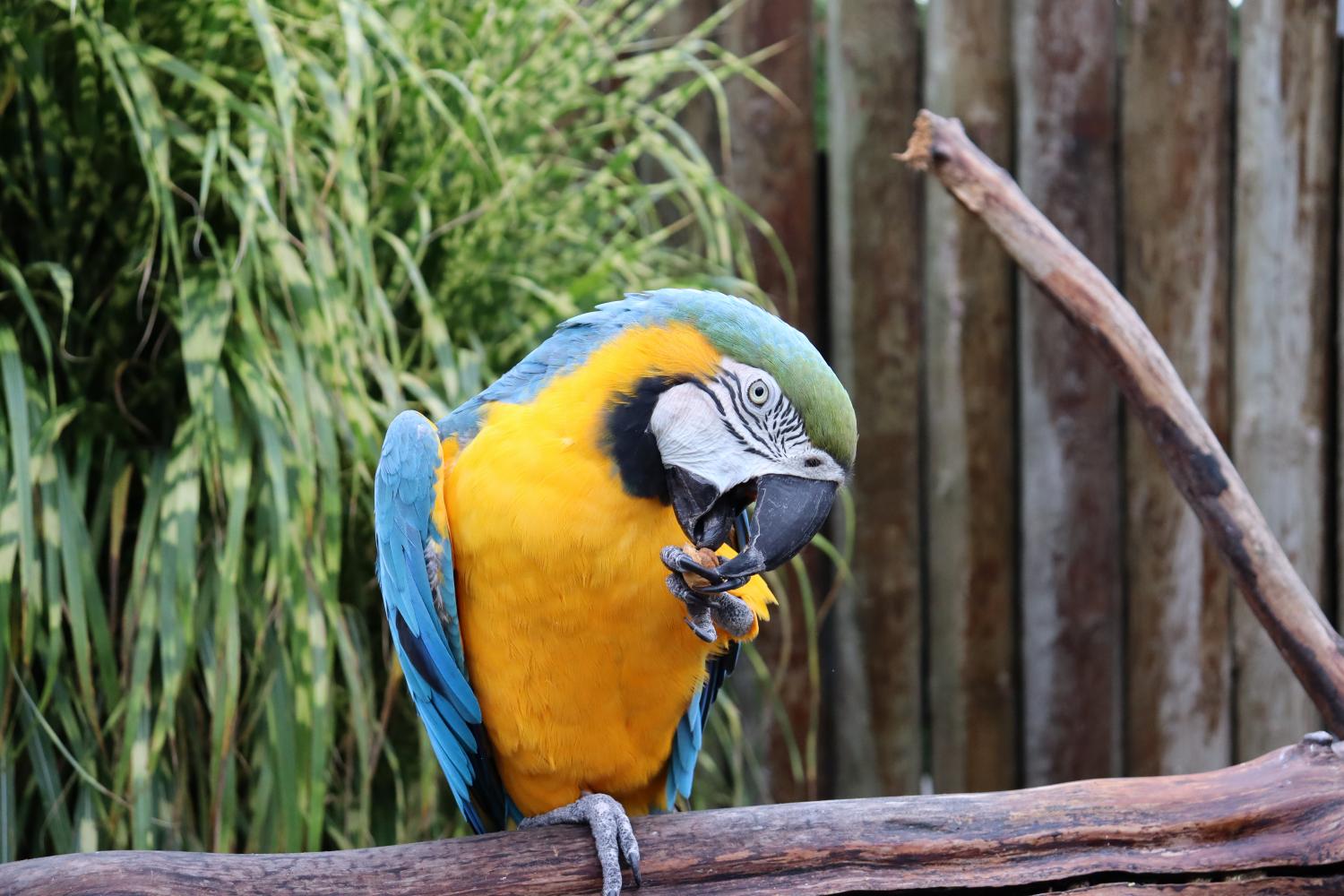
Fruits from various palms, nuts, leaf-buds, and occasionally nectar. Forages in tops of forest canopy.

Reproduction
Builds nests in large, dead moriche palm tree cavities. Breeding season December-February in Columbia and February-March in Surinam. Clutch size 2-4 eggs. Incubation approximately 25 days with chicks fledging around 90-100 days

Conservation
Status:
Listed on IUCN: LEAST CONCERN
Population Trend: DECREASING
Efforts:
Listed on CITES Appendix II. Main threats due to habitat loss and unsustainable trapping for illegal pet-trade. Species has been heavily traded since 1981. Estimated of over 60,000 traded in 2015. A third of their habitat has been destroyed. Between 1999 and 2003, wild-caught blue and gold macaws were translocated from Guyana to Trinidad, in an attempt to re-establish the species in a protected area around the Nariva swamp.

Important Facts

Have been observed to steal nesting sites from the critically endangered Blue-throated macaw.
Usually found in pairs but can often congregate in flocks of up to 25 birds
Will fly as far as 15 miles to forage.
Sources
IUCN: REDLIST
World Parrot Trust
BirdLife International
Birds of the World: The Cornell Lab of Ornithology
A Guide to Parrots of the World
The Large Macaws



